Effective communication is essential in any situation. Whether you are trying to communicate with a colleague, customer, or family member, understanding different types of communication styles can help ensure that your message is heard and understood.
From assertive to passive communication styles, each type has its own strengths and weaknesses. Knowing when and how to use each style can help you convey your thoughts in the most effective manner possible. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of communication styles and discuss when and how to use them for maximum success.
What are communication styles?
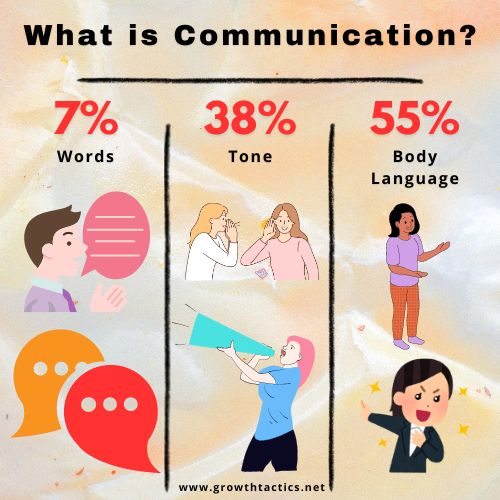
There are various communication styles, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Some people communicate best through words, while others prefer to use body language and tone of voice. People with different communication styles often have different perceptions of what is effective in conveying their ideas.
Some people are very expressive with their body language and facial expressions, which can be interpreted as intimidating or confrontational to others. Others may prefer to remain relatively silent and use only subtle body language cues or no body language at all. In general, the goal of effective communication is to get the message across without offending or alienating the recipient.
Why are communication styles important?
Communication styles are important because they can influence how people feel about and interact with one another. Different communication styles can lead to different outcomes, such as improved relationships or even conflict. Understanding someone’s communication style and your own is important in order to better understand their intentions and interactions.
What’s the most effective communication style?
There is no single definitive communication style that works best for every situation. Each communication style has a time and place, and the right style for a given situation will depend on the individuals involved, the message being conveyed, and the culture of the organization.
4 Types of Communication Styles
Passive Communication
Passive communication is a style of communication in which the communicator does not actively attempt to engage in the conversation. This can be done through body language, eye contact, and vocal tone.
For example, imagine you are in a meeting and a colleague suggests a project idea. Instead of sharing your opinion, you avoid eye contact, keep a neutral expression, and simply nod along.
Passive communication can be effective when you want to avoid conflict or when you lack the time or energy to communicate effectively. However, it can also lead to frustration and misunderstandings if used too often.
Aggressive Communication
An aggressive communication style is a type of communication where the speaker behaves in an aggressive or offensive manner, often without any real intention of achieving the desired outcome. This can be damaging to relationships and can lead to arguments which can be costly for both parties involved. Especially if this is used too often when talking to others.
Body language is a major part of aggressive communication and can be used to convey a number of different messages. For example, crossing one’s arms may indicate that the person is feeling defensive and may not want to listen to what the other person has to say. On the other hand, crossing one’s legs may suggest that the person is feeling uncomfortable and wants to end the conversation as soon as possible.
Passive-Aggressive Communication
Passive-aggressive communication is a type of communication in which someone behaves in a passive manner initially with the hope of achieving a desired outcome without having to confront or openly express their feelings. The person may also communicate indirectly, using non-verbal signals such as body language.
For instance, imagine you ask your friend for help with moving some furniture, and they say, “Sure, I guess I can help,” but their tone is reluctant. They might sigh heavily or drag their feet while helping.
This type of communication can be frustrating for the receiver, as they may not receive the support they need or want. It can also be damaging to relationships if not properly dealt with.
Assertive Communication
Assertive communication is a communication style in which the individual expresses themselves clearly and honestly, with body language and eye contact. It is considered to be more effective than passive or non-assertive styles, as it allows for clarification and resolution of conflicts.
Body language can be used to convey assertiveness, such as maintaining a standing posture, keeping one’s arms close to the body, or keeping a firm grip on objects. Eye contact can also be important in assertive communication, as it shows that the individual is engaged in the conversation. Gestures can also be used to communicate assertiveness, such as using an open hand to show that there is no threat or anger present.
Communicating with other styles

How to communicate with an aggressive style
When trying to communicate with someone who has an aggressive style, it is important to use caution. It can be tempting to respond with an aggressive tone ourselves, in order to get the point across, but this could backfire. Instead, try and maintain a calm and rational approach. Explain your points calmly and concisely, and avoid sounding defensive or argumentative. If the other person is not willing to listen or cooperate, it may be best to steer clear altogether.
How to communicate with a passive style
When trying to communicate with someone who uses a passive communication style, it is important to be aware of when and how to use active and passive voice.
Active voice is typically used when the speaker wants to take control of the conversation or make themselves the focus. For example, “John won the race” is an example of an active sentence.
Passive voice, on the other hand, is used when the speaker wants to allow others to take control of the conversation or make themselves the focus. For example, “The race was won by John” is an example of a passive sentence.
How to communicate with a passive-aggressive style
When trying to communicate with someone who uses a passive-aggressive style, it can be difficult to know when and how to react. The best approach is to be aware of the signs and be patient. If the person begins to exhibit passive-aggressive behaviors in response to your attempts at communication, it may be best to avoid further interaction until a later time.
How to communicate with an assertive style
When communicating with someone who has an assertive style, it is important to be aware of when and how to use this type of communication. Assertive people are confident in who they are and what they want. They often take action to get what they want, which can be a challenge for those who do not understand or agree with their methods.
There are several ways to communicate with someone who has an assertive style. It is important to be aware of the person’s feelings and the situation at hand before speaking. If the person is calm and rational, it is usually best to listen without interruption. If the person becomes agitated or angry, it may be best to back off and wait for them to calm down. In either case, it is important to respect the other person’s right to express themselves in their own way.
Different Forms of Communication and How Communication Styles Affect Them
Here, we’ll explore different forms of communication and how various communication styles can impact them.
Verbal Communication
Verbal communication involves speaking directly. This can encompass in-person conversations, phone calls, or video calls.
- Assertive Communication Style: As an assertive communicator, you are clear and direct. You confidently state your needs while also listening to others. This leads to mutual respect and understanding.
- Passive Communication Style: Passive communicators tend to avoid speaking up. You might find it difficult to express your needs, often leading to frustration and unmet expectations.
- Aggressive Communication Style: Aggressive communicators dominate conversations. Your tone might be confrontational or intense, which can intimidate others and lead to conflict.
- Passive-Aggressive Communication Style: As a passive-aggressive communicator, you appear passive on the surface but act out indirectly. This creates confusion and misunderstanding.
Non-Verbal Communication
Non-verbal communication includes gestures, body language, facial expressions, and eye contact. These often speak louder than words.
- Assertive Communicator: Your body language is open and relaxed. You make comfortable eye contact, and your facial expressions match your words.
- Passive Communicator: You might avoid eye contact and have a closed-off body posture. Others might see you as withdrawn or indifferent.
- Aggressive Communicator: Your gestures can be too strong or exaggerated. This may make others feel uncomfortable or threatened.
- Passive-Aggressive Communicator: Mixed signals are a hallmark here. You might smile while saying something negative, leading to confusion.
Written Communication
Written communication encompasses emails, reports, memos, and messages.
- Assertive Style: Your writing is clear, respectful, and concise. You get your point across effectively without unnecessary fluff.
- Passive Style: You might be too vague in your writing. Important details could be missed, leading to misunderstandings.
- Aggressive Style: Your writing could come off as rude or demanding. This can alienate your audience and reduce cooperation.
- Passive-Aggressive Style: Your tone might be confusing. Sarcastic or ambiguous remarks can lead to misinterpretation.
Visual Communication
Visual communication uses images, graphs, and charts to convey information.
- Assertive Communicator: Your visuals are clear and straightforward. They support your message without overwhelming your audience.
- Passive Communicator: Your visuals might lack impact or clarity. This can make your message less effective and harder to understand.
- Aggressive Communicator: Over-complicated visuals can overwhelm and confuse others, rather than elucidating the information.
- Passive-Aggressive Communicator: Confusing or misleading visuals can obscure your real message and intentions.
Use this knowledge to become a better communicator, strengthen your relationships, and enhance overall workplace harmony. Your communication skills define how successful and productive your interactions will be. By adopting an assertive communication style, you can ensure effective and respectful exchanges, paving the way for better collaboration and results.
Additional Tips to Improve Communication
Improving your communication skills can strengthen your relationships and help you succeed. Here are some simple tips to get you started.
Listen Actively
Pay full attention to the speaker. Nod and make eye contact. Don’t interrupt. Show that you are genuinely interested.
Be Clear and Concise
Keep your message short and straightforward. Avoid jargon and complex words. Make sure your point is easy to understand.
Use “I” Statements
Express your feelings and thoughts using “I feel” or “I think”. This makes your message personal and less accusatory.
Don’t Assume
Ask questions if you are unsure. Don’t make assumptions about what others are thinking. Clarify for a better understanding.
Manage Your Emotions
Stay calm, even if the conversation gets tense. Take deep breaths. Keep your emotions in check to avoid misunderstandings.
Practice Empathy
Put yourself in the other person’s shoes. Try to understand their perspective. Show that you care about their feelings.
Give and Receive Feedback
Offer constructive feedback. Also, be open to receiving feedback from others. This can help improve your communication and relationships.
Be Aware of Non-Verbal Cues
Pay attention to body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. These can convey a lot of information.
Improving communication takes practice. Start with these tips and observe how your interactions improve. Good communication can lead to better connections and understanding.
Quiz: Identify Your Communication Style
Take this quiz to discover your dominant communication style. Answer each question honestly to get the most accurate results. For each statement, choose the option that best describes you.
Questions
- How do you handle disagreements?
- a) I avoid them at all costs.
- b) I try to find a middle ground.
- c) I become very assertive and push my point of view.
- d) I agree openly but internally harbor resentment.
- When speaking in a group, I typically:
- a) Listen more than I talk.
- b) Participate but also encourage others to speak.
- c) Dominate the conversation.
- d) Agree with others but then speak negatively about it later.
- How do you express your needs to others?
- a) I don’t usually say what I need.
- b) I state my needs clearly but respectfully.
- c) I demand what I need.
- d) I hint at my needs and get upset if they’re not met.
- When receiving criticism, I tend to:
- a) Stay silent and take it personally.
- b) Listen carefully and use it to improve.
- c) Defend myself aggressively.
- d) Agree with the criticism but talk negatively about the person later.
- How do you make decisions in a group setting?
- a) I let others decide.
- b) I facilitate discussions to reach a consensus.
- c) I make the decisions and expect others to follow.
- d) Go along with the group but complain afterward.
- In a work environment, I usually:
- a) Keep to myself and avoid conflict.
- b) Collaborate and communicate openly with my colleagues.
- c) Take charge and lead the team.
- d) Agree with others but speak negatively when they’re not around.
Scoring
Count the number of times you picked each letter:
- Mostly A’s: Passive Communication Style
- You tend to avoid expressing your own opinions and needs. You might benefit from learning to assert yourself more.
- Mostly B’s: Assertive Communication Style
- You express your needs and opinions clearly and respectfully. You balance your rights with the rights of others.
- Mostly C’s: Aggressive Communication Style
- You tend to dominate conversations and prioritize your own needs over others. You might benefit from practicing empathy and listening more.
- Mostly D’s: Passive-Aggressive Communication Style
- You may agree outwardly but harbor resentment and express it indirectly. Working on being more straightforward and honest can improve trust and relationships.
Understanding your communication style can help improve your interactions with others. Use this insight to enhance your communication skills and build stronger relationships.
Wrapping Up
Successfully communicating with individuals who have different styles requires tailored approaches. For instance, staying calm with aggressive communicators, being clear with passive ones, understanding cues from passive-aggressives, and respectfully acknowledging assertive communicators can enhance the effectiveness of interactions.
By understanding and appropriately leveraging these styles, you can improve both personal and professional interactions, fostering better communication, stronger relationships, and more successful conflict resolution.
With this new-found knowledge, take a moment to look inward and reflect on your current communication style. Are you assertive, passive, aggressive, or passive-aggressive? Identifying your style is the first step toward improvement.
Did you enjoy this article on communication styles? Please share and subscribe below.